What is a Blood Sugar Test Kit?
Definition
A Blood Sugar Test Kit, also known as a glucose meter or glucometer, is a medical device used to measure glucose awareness in the blood. This device is mainly critical for people with diabetes, a condition characterized by the body’s inability to produce or properly use insulin, leading to unusual blood sugar Test Kit levels. By presenting a brief and accurate degree of blood glucose stages, those kits play a crucial function in diabetes management.
Purpose
A blood sugar check package assists individuals in revealing their blood glucose levels regularly. This monitoring is essential for dealing with diabetes, as it permits customers to:
- Adjust their diet, bodily pastime, and remedy based totally on actual-time glucose readings.
- Detect and promptly reply to excessive (hyperglycemia) or low (hypoglycemia) blood sugar levels.
- Track patterns and developments in blood sugar levels to better understand how various factors
- affect their glucose degrees.
- Share correct facts with healthcare providers to tailor remedy plans more correctly and prevent complications related to out-of-control diabetes.
Components of a Blood Sugar Test Kit
A typical blood sugar test kit consists of the following components:
- Glucose Meter: This tool reads and shows the blood glucose stage. It is regularly compact and portable, designed for ease of use.
- Test Strips: Small, disposable strips containing chemical substances that react with blood glucose. Each strip is used as soon as possible, after which it is discarded.
- Lancet Device: A small, spring-loaded instrument used to prick the pores and skin (usually a fingertip) to attain a drop of blood. The tool is designed to be as painless as viable.
Lancets are tiny, sharp needles used with the lancet device to prick the pores and skin. Like test strips, lancets are disposable and should be used handily once. - Control Solution (Optional): A liquid with a recognized glucose awareness is used to test the accuracy of the glucose meter and test strips.
- Data Management Tools (Optional): Some current glucose meters have software or apps that track and examine blood sugar records over the years. This equipment helps manage and share information with healthcare companies.
How Does a Blood Sugar Test Kit Work?

The Science Behind Glucose Monitoring
Blood sugar test kits function based totally on the principle of electrochemical detection. A blood pattern on a test strip interacts with specific chemicals, generating an electrical signal that the glucose meter reads and converts into a glucose awareness cost. Here’s a detailed look at the technological know-how behind it:
- Chemical Reaction: The check strip incorporates enzymes, usually glucose oxidase or dehydrogenase. When a drop of blood is implemented, these enzymes react with the glucose in the blood.
- Electrical Signal Generation: This reaction produces an electrical cutting-edge proportional to the quantity of glucose within the blood sample. The extra glucose present, the more potent the current.
- Signal Measurement: The glucose meter measures the electricity in the present day. Inside the meter, an included circuit measures the signal.
- Conversion to Glucose Level: The meter converts this electrical into a numerical fee representing the blood glucose concentration, typically in milligrams in keeping with deciliter (mg/dL) or millimoles per liter (mmol/L).
This process happens within seconds, quickly and accurately measuring blood glucose levels.
Items Included in Most Blood Sugar Test Kits:
- Glucose Meter: This is the primary device for reading blood sugar Test Kit levels. It displays your glucose concentration, usually in mg/dL or mmol/L.
- Test Strips: These are inserted into the glucose meter. After applying a small blood sample, each strip is used once to read your blood sugar Test Kit level.
- Lancing Device and Lancets: A lancing device is used to prick the skin (usually on a fingertip) to obtain a blood sample. Lancets are small, sharp objects loaded into the lancing device.
- Control Solution: Used to ensure the glucose meter and test strips are working correctly and providing accurate readings.
- Batteries: Most glucose meters operate on batteries, which need to be checked and replaced periodically.
- You are carrying a Case, a convenient way to store and transport your meter, strips, lancing device, and other supplies.
Steps for Using a Test Kit
Using a Blood Sugar Test Kit involves several straightforward steps to ensure an accurate reading. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Prepare the Equipment: Ensure you have all necessary components: a glucose meter, test strips, lancet device, and lancets. Wash and dry your hands thoroughly to prevent contaminants from affecting the test results.
- Insert a Test Strip: Take a test strip from its container and insert it into the glucose meter. Once the strip is inserted, the meter will usually turn on automatically.
- Load the Lancet Device: Insert a new lancet into the lancet device. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions to load and prime the device.
- Obtain a Blood Sample: Select a fingertip and use the lancet device to prick the side of your fingertip. Some meters allow alternative site testing (such as the palm or forearm), but fingertip testing is generally the most accurate. Gently squeeze your fingertip to form a small drop of blood.
- Apply the Blood Sample: Touch the threshold and examine the strip on the blood drop. The strip will draw in the blood through capillary motion.
As the meter’s instructions indicate, ensure the strip absorbs enough blood to fill the required area. - Read the Results: Wait for the meter to process the sample. This usually takes a few seconds. The meter will display your blood glucose level.
- Record the Results: Many glucose meters store your readings automatically. However, it is good practice to record your results in a logbook or app, noting the time and any relevant details (e.g., before/after meals, physical activity).
- Dispose of Used Supplies: Safely dispose of the used lancet and test strip. Many people use a sharps container for lancets to ensure safe disposal.
High Blood Sugar (Hyperglycemia): Understanding, Managing, and Preventing
What is the Best Diabetes Test Kit?
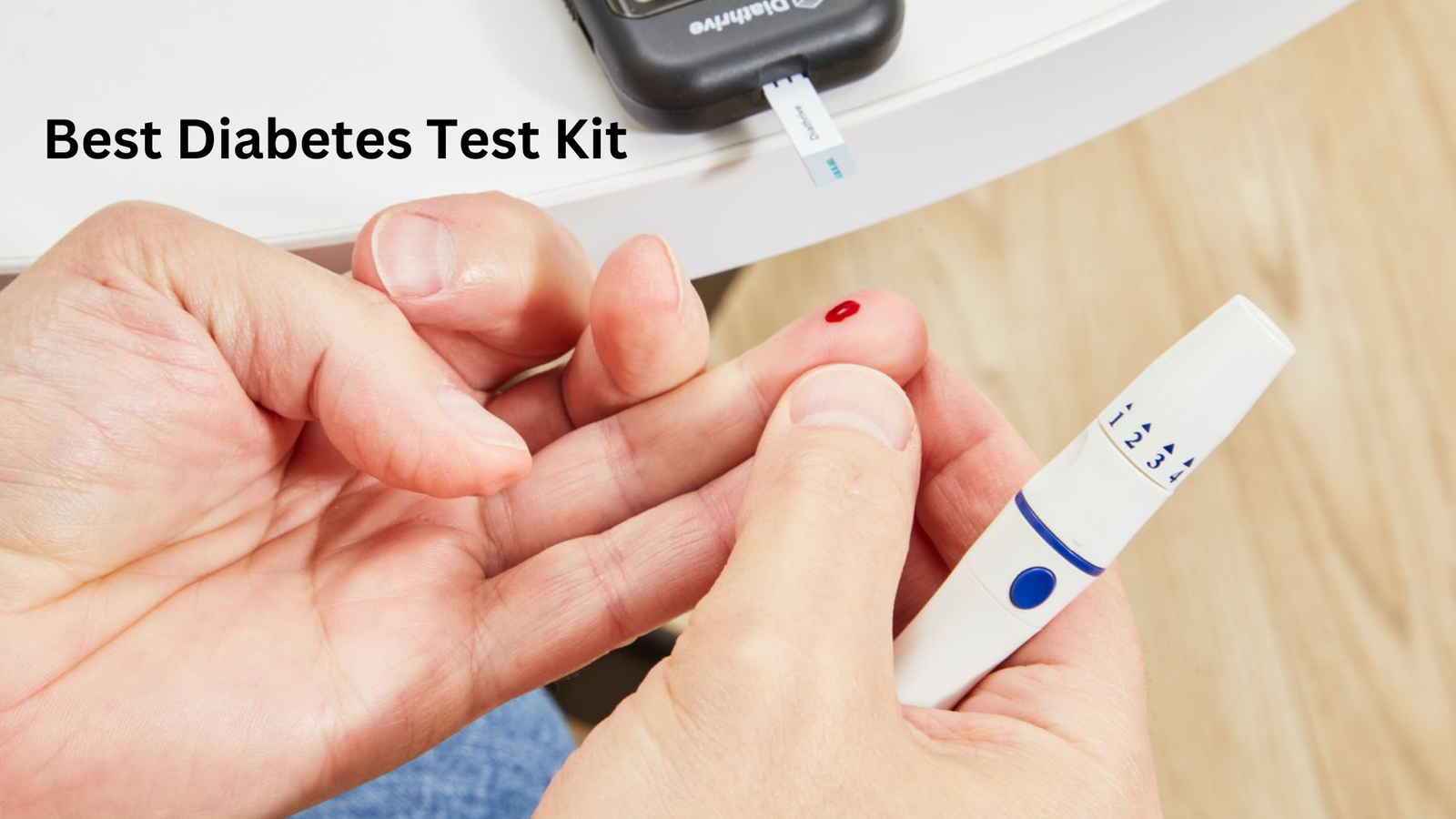
Choosing the best diabetes blood Sugar Test Kit depends on individual needs, preferences, and specific health requirements. There are several top-rated diabetes test kits available, each with its unique features and benefits. Here are some of the first-rate alternatives:
1. Accu-Chek Guide
The Accu-Chek Guide is known for its accuracy, ease of use, and convenience.
Features:
- Spill-resistant test strip vial
- Bluetooth connectivity to sync with the mySugr app
- Large, easy-to-read display
- Backlit screen for low-light testing
Pros:
- High accuracy and reliability
- User-friendly design
- Data management features
Cons:
- Test strips can be expensive
2. OneTouch Ultra 2
The OneTouch Ultra 2 is popular due to its simplicity and reliability.
Features:
- Fast results in just 5 seconds
- Requires a small blood sample
- Memory to save up to 500 check consequences
- Easy-to-navigate menu
Pros:
- Affordable and widely available
- Quick and accurate results
- Large memory for tracking data
Cons:
- Lacks advanced connectivity features
3. Freestyle Libre
The Freestyle Libre is a flash glucose monitoring system that provides continuous glucose readings.
Features:
- The sensor is worn at the lower back of the top arm for up to fourteen days
- No fingerstick calibration is required
- Glucose readings every minute
- Reader device or smartphone app to scan the sensor
Pros:
- Continuous and comprehensive glucose monitoring
- No need for regular fingersticks
- Provides trends and patterns in glucose levels
Cons:
- Higher initial cost compared to traditional glucometers
- The sensor desires to be replaced every 14 days
4. Dexcom G6
The Dexcom G6 is a continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) system that offers real-time glucose monitoring.
Features:
- Sensor and transmitter for continuous glucose data
- No fingerstick calibration is required
- Integrates with various insulin pumps and apps
- Alerts for high and low glucose levels
Pros:
- Real-time, continuous monitoring
- High accuracy and no need for calibration
- Customizable alerts for glucose trends
Cons:
- Expensive compared to traditional glucose meters
- Requires a prescription
5. Contour Next EZ
The Contour Next EZ is praised for its high accuracy and simplicity.
Features:
- Second-chance sampling allows adding more blood to the same strip if the first sample is insufficient
- No coding required
- Fast results in 5 seconds
- Large, easy-to-read display
Pros:
- High accuracy with Second-Chance Sampling
- Affordable and widely available
- Easy to use
Cons:
- Limited advanced features compared to other high-end models
Choosing the Right Kit for You
When selecting the best diabetes test kit, consider the following factors:
- Accuracy: Ensure the device provides consistent and accurate readings.
- Ease of Use: Look for a kit that is easy to handle and use, especially if you have dexterity issues.
- Cost: Consider the cost of the device and the ongoing cost of test strips and lancets.
- Features: Decide if you need advanced features like data connectivity, continuous monitoring, or ample memory storage.
- Insurance Coverage: Check if your insurance covers the cost of the device and supplies.
Types of Blood Sugarest Kitoional Glucometers
Traditional glucometers are a common type of blood sugar test kit. They are portable, easy to use, and relatively affordable, providing a quick snapshot of your blood sugar levels.
Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs)
CGMfitting more advanced devices that continuously monitor blood glucose levels throughout the day and night. They use a sensor inserted under the skin to measure glucose levels in the interstitial fluid. CGMs provide real-time data and can alert users to highs and lows.
Flash Glucose Monitors (FGMs)
FGMs, like the Freestyle Libre, are similar to CGMs but do not provide continuous real-time data. Instead, users scan a sensor with a reader device to get glucose readings. FGMs are often more affordable than CGMs and still provide detailed glucose level trends.
Conclusion
Regular Blood Sugar Test Kit checking is critical to managing diabetes and preserving correct fitness. Using a blood sugar take-a-look-at kit, you could display your blood glucose stages, make knowledgeable choices regarding your weight loss program and lifestyle, and save you headaches associated with diabetes. Choosing the fitting blood sugar check package, following first-rate practices for accurate trying out, and consulting with your healthcare provider allows you to achieve premier blood sugar control and improve your standard well-being.
FAQS About Blood sugar test kit
Q1. Can stress cause hyperglycemia?
A: Yes, stress can increase blood sugar Test Kit levels by triggering the release of stress hormones like cortisol and adrenaline.
Q2. How often should I take a look at my blood sugar?
A: The testing frequency depends on the type of diabetes and the treatment plan. People with kind 1 diabetes can also want to check multiple instances a day, at the same time as those with kind 2 diabetes may additionally take a look at much less regularly.
Q3. Are there any side effects of frequent testing?
A: can sometimes cause discomfort or minor skin irritation at the testing site. Using different fingers and proper techniques can help minimize these effects. In rare cases, excessive testing might lead to calluses or scarring, but this can be managed with appropriate care and rotation of testing sites.
Q4. How accurate are home blood sugar test kits?
A: Home blood sugar test kits are generally accurate when used correctly. However, expired test strips, improper storage, and incorrect usage can affect accuracy. Most modern glucometers have a margin of error of around ±15%, which is considered acceptable for home testing. Regular calibration and following producer tips can help ensure dependable results.

